Core Web Vitals: How To Measure and Improve Them for Ranking Signals?
Web Vitals and Core Web Vitals are the best available signals for measuring the quality of experience throughout the web right now, but they aren't perfect, and future enhancements or additions should be expected.
Google announced a page experience upgrade to their ranking the algorithm in May 2020.
The Core Web Vitals apply to all websites and appear in a variety of Google tools. Changes to these metrics will have far-reaching consequences; as a result, developers should anticipate the Core Web Vitals' definitions and thresholds to remain stable, and updates to occur on a regular, annual schedule.

The purpose of this update is to:
improved user experience, more organic ranking signals will be included. The update will be phased in starting in mid-June 2021.
 |
| Source: developers.google.com |
The Core Web Vitals will be included in Google's ranking algorithm as part of the page experience signals. These three Core Web Vitals are indicators of a page's load time, visual stability, and interactivity.
What Is Core Web Vitals?
Google considers Core Web Vitals to be a set of particular elements that contribute to a webpage's overall user experience. Three specific page performance and user interaction statistics make up Core Web Vitals:
- largest contentful paint (LCP)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
- First Input Delay (FID)
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This is known as the appearance of the largest above-the-fold content item.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This indicator indicates how unexpected layout adjustments (ads, pop-ups, etc.) impair the visual stability of a page.
- First Input Delay (FID): This is a metric that quantifies how long does it take a browser to process the first user interaction on a page.
In a nutshell, Core Web Vitals are a subgroup of variables that will be included in Google's "page experience" score. essentially, how Google evaluates your website's overall user experience.
Additional Factors Which Affect search signals for page experience.
Besides this, there are additional factors that affect the page experience.
- Mobile-friendliness - This refers to ensuring that websites "shrink" to fit the screen size of a mobile phone.
- Safe-browsing - This entails ensuring that your website is free of viruses and spyware.
- HTTPS - This defines the importance of web pages and the use of the SSL/TLS protocol to make the HTTP of a website safe. It's critical to have the small padlock icon before you start working on your website's design!
- No intrusive interstitials - This refers to intrusive pop-up adverts on mobile devices that obstruct or obscure the majority, if not all, of the content on the website, making it impossible for the user to read the content, perhaps leading to a negative experience.
Google Search Console is a useful tool. You'll discover an option under "Experience" in this tool that will take you to a report that examines your website's performance against the Core Web Vitals elements.
How can you determine if your website's Core Web Vitals elements are working properly?
Step 1: First visit Google Search Console, which is a useful tool for core web vitals assessment. Click the “Start now” button to head to the Google Search Console dashboard.
Step 2: You will discover an option “Core Web Vitals” tab under "Experience" in this tool that will take you to a report that examines your website's performance against the Core Web Vitals elements.
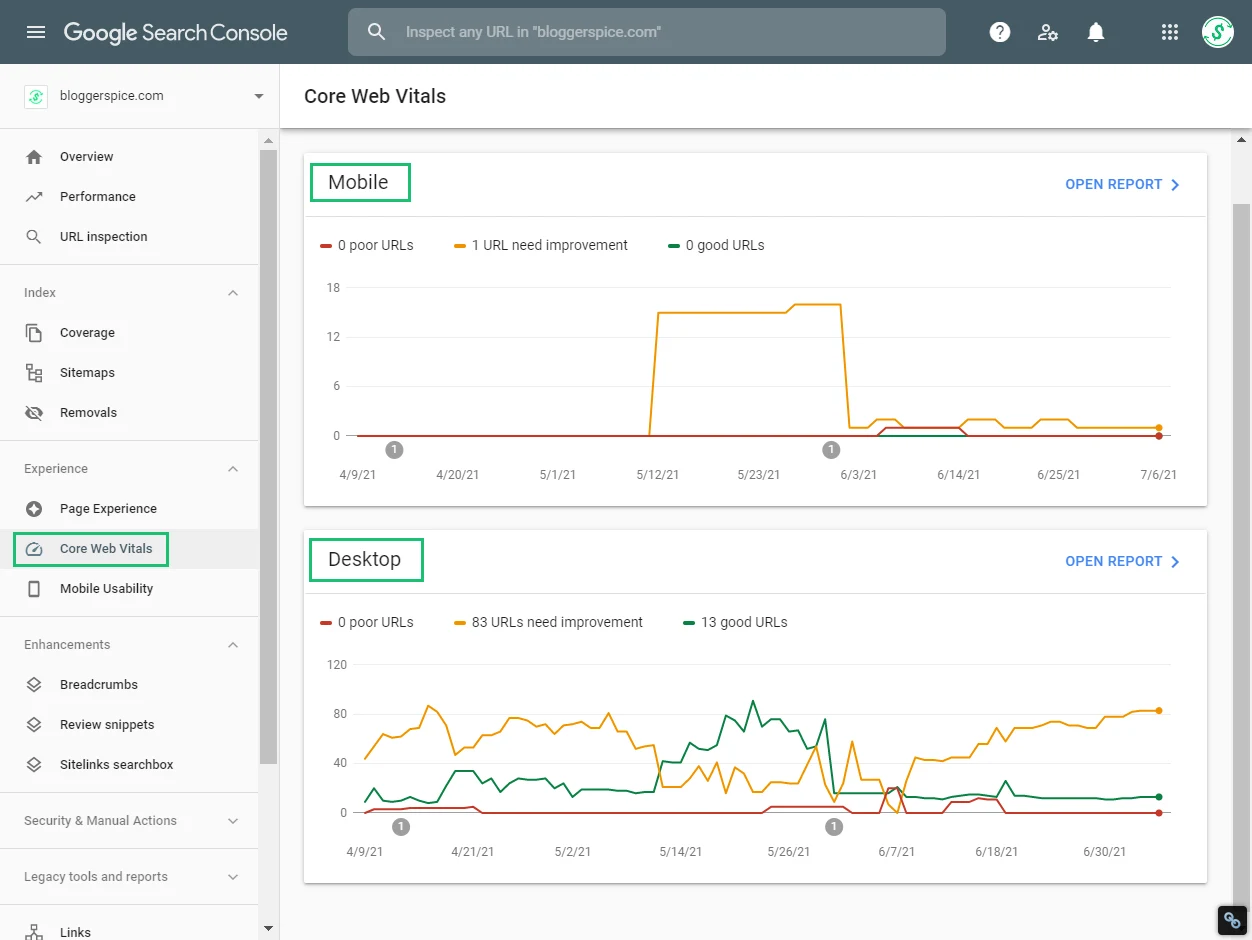
Step 3: The Core Web Vitals tool in Google Search Console will provide you with a list of the URLs that are affected and which elements need to be upgraded. Improved load time (LCP), interactivity (FID), or visual stability (CLS) could all be part of this.
How Can You Assess Your Website's Core Vitals?
Now that I'm sure you've heard of Google Core Web Vitals, how can we figure out where our pages rank?
Fortunately, there are a few methods for analyzing your website.
The Core Web Vitals matrices can be found using a variety of technologies such as Google Search Console, PageSpeed Insights, and Lighthouse.
If you're not familiar with these tools, the simplest option is to enter the URL of your website into a specific PageSpeed Insights tool.
Also, check your overall score out of 100 for both mobile and desktop. This is the total page speed score, which gives you a good idea of how fast your website is.
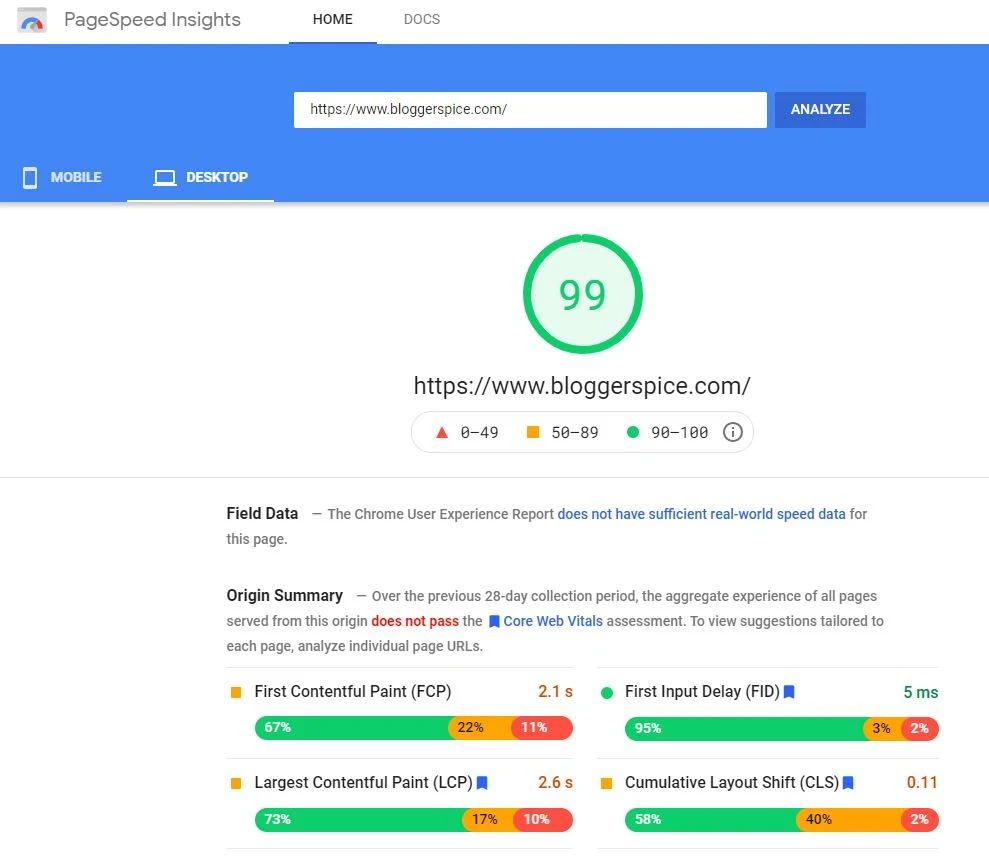
After checking the report from the Google search console you can use PageSpeed Insights to check the affected pages after you're familiar with the affected URLs on your website. Based on real-life statistics from Google Chrome browsers, this application will provide mobile and desktop speed insights.
The PageSpeed Insights tool will show you a summary of all the issues on particular pages, which will help you get started on improving your site and passing the Core Web Vitals evaluation.
The Chrome Extension of Core Web Vitals.
There are several Google Chrome add-on that can be used to perform a rapid Core Web Vitals check. All extensions are good.
1. Web Vitals
2. Core Web Vitals Annotations
3. Core Web Vitals
The extension does a quick LCP, CLS, and FID audit for you.
The extension now has a new UI and a lot more relevant information thanks to a recent upgrade. For example, the audit analyses how well the page performs on your device to how well it performs for other users.
The Web Vitals provides the real-user data.
How to Optimize for the Most Important Web Factors?
It's time to optimize your site's Core Web Vitals after you've measured them.
How to improve the First Contentful Paint (FCP) score?
To provide an outstanding user experience, sites should aim to show the First Contentful Paint loading time within 1.8 seconds or less. The 75% of page loads, divided across mobile and desktop devices, is an excellent benchmark to measure to ensure you're hitting this target for the majority of your consumers.
Refer to the following performance tips to discover how to enhance FCP in general for any site:
- Render-blocking resources should be removed.
- CSS should be minimized.
- Remove any CSS that is no longer in use.
- Connect to the appropriate origins beforehand.
- Reduce the time for the server to respond (TTFB)
- Multiple page redirects should be avoided.
- Requests for key preloading
- Stay away from massive network payloads.
- With an efficient caching policy, serve static assets.
- Excessive DOM size should be avoided.
- Reduce the depth of essential requests.
- Ensure that text is visible while the Webfont is loading.
- Reduce the number of requests and transfer sizes.
How to Make Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) Time Faster?
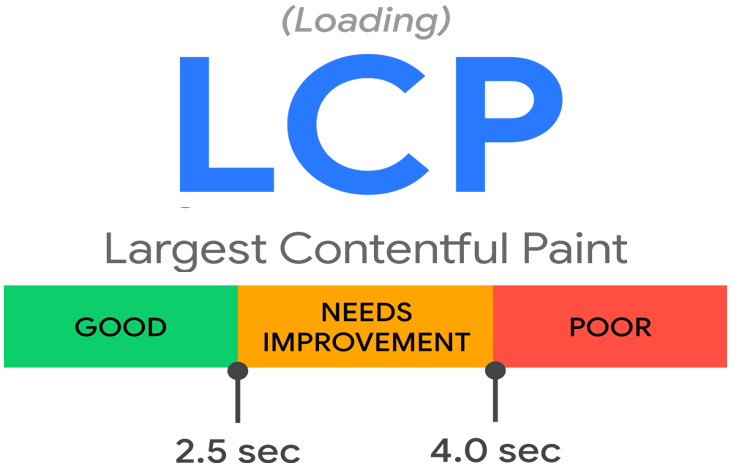
Here are some suggestions for lowering your LCP:
- Upgrade your hosting plan - For site speed, a quick server response time (TTFB) is critical. Consider moving to a dedicated hosting plan if you're on a slow shared hosting server.
- Critical CSS should be implemented - Finding the CSS required to load above-the-fold information and inlining it in the head tag is known as critical CSS. This method enhances both actual and perceived performance.
- Optimize your Blog images - Website Images must be compressed, scaled, and converted to the correct format, which is often the most common cause of slow web pages.
- Load hero images First - Because hero photos are frequently the most important above-the-fold elements, loading them as quickly as possible is critical for the user experience. LCP can be greatly reduced by using link rel="preload", especially for hero images loaded with CSS or JavaScript.
How to Resolve Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) Problems?
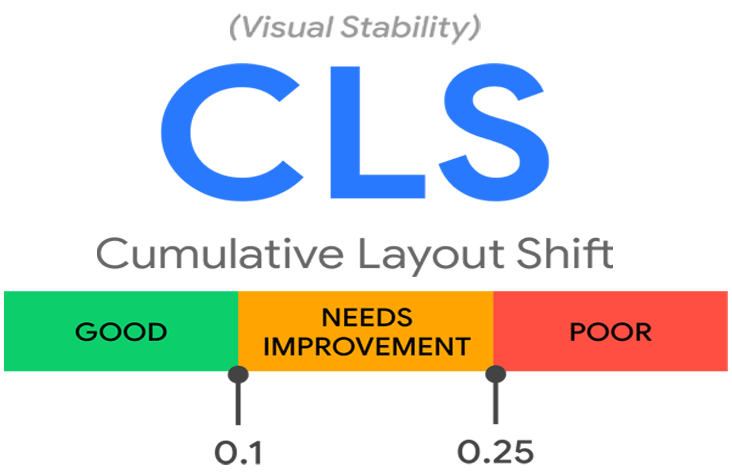 Here are a couple of tweaks that can drastically reduce layout shifts:
Here are a couple of tweaks that can drastically reduce layout shifts:
- Don’t place ads and pop-ups above other content - Ads and pop-ups should not be placed above other content. The GIF above the fold isn't a good idea. When information is placed at the top of a page, everything below it shifts, giving in a low CLS score.
- Fix the height and width of your image and Videos - Images and videos should have width and height attributes. These properties aid the browser in determining the appropriate amount of space for each element ahead of time. This considerably eliminates layout shifts.
- Make room for advertisements, iFrames, and dynamic content - Ads, iFrames, and dynamic content should all have their own place. These items, like photographs and videos, might cause layout adjustments if they aren't given enough room. Use containers that are the right size and have enough overflow: to prevent the content from overflowing its container; hidden property to prevent the content from overflowing its container;
- Improve font delivery - Layout shifts and flashes of invisible text can be avoided by combining link rel="preload" and font-display: optional.
How to Resolve First Input Delay (FID) Problems?

- Long tasks should be broken up - As I already stated, this should be your top priority. Long Tasks obstruct the Main Thread's ability to respond to user inputs in a timely manner. You may dramatically enhance the performance of your website by dividing them up.
- Compress and minify code files - Whitespace and line breaks are removed from the code during minification. Compression also changes the size of code files, making them smaller. These strategies are used by default by several hosting and CDN providers.
- Non-essential third-party scripts should be postponed or removed - Third-party scripts can cause your own scripts to fail to run on time. Consider which scripts offer the most value to the user and rank them accordingly. Ad and pop-up scripts aren't always at the top of the priority list.
- Make use of web workers - You can use web workers to run scripts in the background without interrupting the Main Thread. It's generally a good idea to move non-UI actions to a background thread.
- CSS should be optimized - While JS is the major enemy in FID, CSS is by default render-blocking. As a result, too much CSS might degrade the user experience. It's also worth decreasing the amount of unneeded CSS on your site, in addition to using Critical CSS and minifying and compressing CSS files.
Conclusion
Already from June 2021, the real-life user experience on any website has become a ranking consideration for Google's algorithm. Google is now utilizing the collection of measures called Core Web Vitals to determine how users interact with websites in the real world. To ensure that your website is ready for the upgrade, use the tools and resources to assess its performance and make any necessary modifications as soon as possible.
The Core Web Vitals are a significant step in making the website a better place for more people. These criteria appear to be here to stay as part of Google's ranking system.
That's why, even if you don't see any problems right now, you should keep an eye on them.


Post a Comment